Nash Equilibrium Poker Heads Up
HeadsUp Push/Fold Nash Equilibrium The charts below show the Nash Equilibrium strategies for two player push-or-fold NLHE. This is a simplified game where the SB is only allowed to go all-in or fold, and the BB can either call or fold when facing a shove. Poker and the Nash equilibrium. If you think about it, that means that every poker situation and poker in general has its own Nash equilibrium. In theory, if everyone plays perfectly, even no-limit hold'em is a solved game. Say in a heads-up 'pushbot' (all in or fold).
- Heads Up Nash
- Nash Equilibrium Chart
- Nash Equilibrium Examples
- How To Find Nash Equilibrium
- Mixed Nash Equilibrium
- Poker Nash Equilibrium
Nash equilibrium is one of the most ubiquitous terms in game theory. It's used everywhere from meetings in small companies through poker strategy materials to the movie 'A Beautiful Mind'. The term gets its name from John Forbes Nash, Jr. a brilliant scientist responsible for many breakthroughs in economics, mathematics and game theory. Basic understanding of the Nash equilibrium can be invaluable in any non-cooperative game involving two or more players and poker certainly falls under that definition.
Game Theory
According to the Nash equilibrium in heads up with ante player on a small blind with 15 big blinds stack should push 48.4% of hands and player on a big blind calls with 30.6% of hands However, in real game, the big blind will not call with this range. Jan 07, 2016 Transition from No-Limit to Fixed-Limit Adapting the Nash Equilibrium for Heads-Up LIMIT Hold' Em Since our concern here isn't Heads-Up No-Limit Texas Hold' Em but Heads-Up Fixed Limit Hold' Em the number of effective BB (Big Blinds) will be different.
Let's start with a brief explanation of the game theory. According to the official definition, game theory is 'the study of mathematical models of conflict and cooperation between intelligent rational decision-makers'. It's the study of human behaviour in strategic settings that has wide applications in economics, psychology, computer science, poker etc. Now that we know what game theory is let's take a step back and figure out what constitutes a 'game'. To have a game you need at least two players, some incentives to play the game (clearly defined outcomes for the players) and rules.
Nash Equilibrium
Another official definition tells us that 'In game theory, the Nash equilibrium is a solution concept of a non-cooperative game involving two or more players, in which each player is assumed to know the equilibrium strategies of the other players, and no player has anything to gain by changing only their own strategy.' In the poker context, it basically means that there's no point in playing anything but the game theory optimal strategy if we know our opponent is also playing a game theory optimal strategy since we can't exploit the GTO strategy.
Real Life Example
To further simplify the idea of Nash equilibrium, let's look at a classic example of prisoner's dilemma. In the hypothetical situation, two people are questioned separately about a crime they both committed. If they both confess to committing the crime they will spend 8 years in prison. If they both decide to keep quiet they will get locked up for a year on some minor charges. If the first player decides to confess (giving up his 'friend' in the process) and the second one lies, the first one will walk free and the first one will spend 10 years in prison (and vice versa).
Free slots for you.
As a poker player, you can easily determine the best strategy in this situation. It makes the most sense to confess since both risk and reward of that play are higher for you than the alternative regardless of the other player's choice. In this particular example confessing is the Nash equilibrium since if we knew that the other player will confess we can't punish him for that play by changing our strategy, we can only punish ourselves. Of course, lying would be better for the group but poker is not exactly a group activity and that's outside of the scope of this article.
Nash Equilibrium HU Poker Chart
Poker is a very, very complicated game. Much more so than the hypothetical situation described above. That's why we still haven't figured out the game theory optimal strategy even for less complicated formats like HU Limit Hold'em (though we're somewhat close in this particular case) and judging from how fast processing power of computers increase from year to year, this won't happen anytime soon for the more complicated formats like 6-max or 9-max Holdem/PLO. However, if we greatly simplified the game and assumed that players in a HU game can only go all-in or fold in the SB position and call or fold in the BB position we can determine the nash equilibrium for that situation:
Heads Up Nash
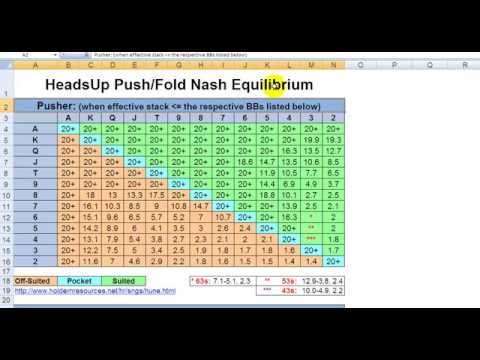 Just like in the hypothetical prisoner's dilemma if we knew that our opponent is following the Nash equilibrium strategy, we can't punish him for that choice and therefore, all we can do is to also follow the strategy. In reality, it's much more complicated than that. Players can, limp and use different raise sizes, they will also rarely if ever use the Nash equilibrium as their push or fold strategy and even if they do so, they will most likely start doing that closer to 8-10bb than 20bb stack size.
Just like in the hypothetical prisoner's dilemma if we knew that our opponent is following the Nash equilibrium strategy, we can't punish him for that choice and therefore, all we can do is to also follow the strategy. In reality, it's much more complicated than that. Players can, limp and use different raise sizes, they will also rarely if ever use the Nash equilibrium as their push or fold strategy and even if they do so, they will most likely start doing that closer to 8-10bb than 20bb stack size. Imagine a player who's on extreme tilt near the end of your head's up match and decides to push every hand. We can call that player with a much wider range than Nash equilibrium would suggest. Conversely, if an extremely nitty recreational player is only willing to push premium pocket pairs no matter the stack size we also shouldn't stick with blindly following the Nash equilibrium table and instead punish his narrow hand selection with frequent small raises.
What is Nash Equilibrium Good for Then When it Comes to Playing Poker?
It's valuable in a couple of ways. It can serve as a baseline for our strategy. As the number of meaningful choices we can make in the game decreases (in the context of poker game this will happen as the stack to pot ratio decreases) it makes more sense to actually follow the equilibrium. While even in today's games we can still exploit players in HU even with stacks as low as 8-10 BB's it's actually not a bad rule of thumb to start using the Nash equilibrium table as our stack reaches that point, especially when we're just starting out or we're playing against a tough competition.
Austin tx. Dealing Poker 7 days a week! Currently accepting all new members to our exclusive private entertainment venue located off Highway 281 North, just outside of San Antonio, Texas. All Stakes Cash games, Texas Hold’m and Omaha tournaments for all skill levels are offered daily. Abby J Card House (poker parlor) is a members-only private club, located in San Antonio, Texas, that provides its members an opportunity to play poker legally. Members pay daily, monthly, or yearly membership dues for access to its poker room.
Nash Equilibrium Chart
the good old fashioned exploitable strategies are still the way to go in almost every form of poker.Nash Equilibrium Examples
More Top Rated Content
How To Find Nash Equilibrium
Articles
- How to Make a Poker Schedule - Tools You Can Use
- Motivational YouTube Videos - Friend or Foe?
- How to Get in the Zone and Play Your Best Poker
Mixed Nash Equilibrium
Coaching Videos
Poker Nash Equilibrium
- Optimizing Sleep for Poker Success
- Hypnotherapy in Poker



